Introduction
Cold sore usually show up on the lips or mouth as a cluster of blisters with a red base. They are also called “fever blisters.” They may be painful and feel itchy, dry, and crusty. If the blisters come back another time, they may cause a tingling feeling before they appear on the skin. The virus that causes them, herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), is very common and spreads very easily. Although the virus is commonly spread by kissing, it may also spread by more casual contact.
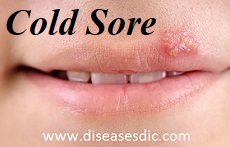
Cold sore on the upper lip
Two kinds of herpes simplex outbreaks may occur: primary and recurrent.
- When your child is first infected with HSV-1, it causes a more severe outbreak. In addition to cold sores, there may be other symptoms such as fever, swollen gums, enlarged lymph nodes, and sore throat.
- Cold sores may come back once in a while. Recurrent outbreaks are much less severe than the primary outbreak. Your child will probably have no fever or other symptoms. However, HSV-1 can cause sores elsewhere on the body.
Stages of cold sore
There are five different stages:
- Tingle
This stage normally lasts between a few hours and a day. The cold sore is invisible at this stage but a tingling or burning sensation may be felt. If an antiviral cream (aciclovir) is applied at this stage it may prevent the visible signs of the cold sore from appearing. Aciclovir attacks the virus and stops it from multiplying.
- Blister:
This stage is characterized by a small group of painful, fluid-filled blisters. These are normally seen on the second day of the cold sore cycle. Here again, treatment with an antiviral cream will reduce the life of the cold sore.
- Ulcer:
Once the small blisters have burst, a weeping ulcer is seen that may last for several days. This stage is also very painful. The clear liquid that is released from the ulcer contains a high number of viral particles and as such is highly contagious.
- Scab:
After about 4 days a thin scab will form, acting as a protective covering for the new skin that is forming beneath. The skin around the scab may dry and crack and even bleed. Moisturising the area will help to reduce this. The scab may also be itchy, but is not contagious at this stage.
- Healing:
After 9 – 12 days the cold sore will have healed. A slightly red/pink area of skin will remain but will quickly fade. Most people who get cold sores will usually experience around 2 – 3 attacks per year although some people may get as many as 12.
History behind cold sores
- Herpes was first formally recognized by Hippocrates (460 to 370 BCE), who wrote about the symptoms of herpes lesions.
- The word herpes is taken from the Greek “herpein,” meaning to creep or crawl. This refers to the way the herpes sores spread over the affected area.
- Later on, in Roman times, the Roman Emperor Tiberius tried to quell an oral herpes outbreak by banning kissing at public celebrations, events, and ceremonies.
- A Roman physician named Celsus developed a treatment method for herpes that involved cauterizing open herpes lesions with a hot iron.
- In 1893, French scientist Emile Vidal proved through experimentation that herpes was transmitted from one person to another.
- In 1884 Louis Duhring, an American dermatologist, confirmed that herpes was different from eczema and pemphigus, which are non-contagious skin conditions.
- Two years later, in 1886, French doctors Charles-Paul Diday and Adrien Doyon published a full-length book about herpes called “The Genital Herpes.”
- Viruses were discovered by Dmitri Ivanovski in Russia in 1893. Although Ivanovski was studying tobacco viruses, not herpes viruses, his research later became important for studying herpes.
- In 1896 German physician Paul Unna develops a way to differentiate herpes from syphilis under a microscope. This is important because previously it was not possible to identify the difference between herpes and syphilis since they often occurred concurrently.
- 1913: Wilhelm Grater, a German ophthalmologist, is able to transmit the herpes virus from an infected person to the cornea of a rabbit and back again to a human. This is named the Grater test, which is used to diagnose herpes until the 1940’s.
- In 1925 an American virologist, Ernest Goodpasture, proves that the herpes virus travels through the nerves, not the blood.
- In 1939, Frank LacFarlane Burnet, an Australian microbiologist, develop the theory of latency, or the fact that the herpes virus resides in the ganglions while there are no symptoms. In 1971 scientists Jack Stevens and Marjorie Cook prove it.
- A French scientist, Arnaud Tzanck develops cryto-diagnosis for herpes, which replaces the Grater test.
- In 1978, the first anti-viral drug, Acyclovir that was safe, non-toxic, and effective is tested in humans. It was developed by Gertrude Elion, and three years later was available commercially.
Epidemiology
More than 3.7 billion people under the age of 50 – or 67% of the population – are infected with herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), according to WHO’s first global estimates of HSV-1 infection published in the journal PLOS ONE.
The new estimates highlight, however, that HSV-1 is also an important cause of genital herpes. Some 140 million people aged 15-49 years are infected with genital HSV-1 infection, primarily in the Americas, Europe and Western Pacific. Fewer people in high-income countries are becoming infected with HSV-1 as children, likely due to better hygiene and living conditions, and are instead at risk of contracting it genitally through oral sex after they become sexually active.
Causes of cold sores
- Any infection, such as a cold, can prompt the virus to show itself
- It is easier for the virus to become active when your immune system (your body’s natural defense) is weakened by another illness
- Trauma, such as a scrape or cut
- Emotional stress
- Sun exposure
- Some women experience active fever blisters only during their menstrual cycle
- Some scientific evidence indicates the herpes virus is inherited
Complications after the onset of cold sore
Cold sores are unlikely to cause complications, except occasionally, in patients with a weakened immune system. Possible complications include:
- Dehydration: This is possible if pain in the mouth and throat makes the patient reluctant to drink.
- Herpetic whitlow: The cold sore virus spreads to other parts of the body, for example, the hands, causing blisters to appear on their fingers, usually through a cut or graze in the skin. Antiviral medications can treat this type of complication.
- Herpetic keratoconjunctivitis: A secondary infection causes the eyes to become swollen and irritated, possibly with sores on the eyelids. Antiviral medication can usually help. Without treatment, the cornea may become infected, resulting in possible vision loss.
- Bacterial infections. Cold sores may become infected with bacteria or may lead to ulcers that take a long time to heal. Sores may become more crusted (yellow or oozing pus).
- Encephalitis: If the virus spreads to the brain, the brain can swell. There is a serious risk of brain damage, and possibly death.
Risk factors of cold sore
People who have weakened immune systems are at higher risk of complications from the virus. Medical conditions and treatments that increase your risk of complications include:
- HIV/AIDS
- Severe burns
- Eczema
- Cancer chemotherapy
- Anti-rejection drugs for organ transplants
Diagnosis of cold sore
The diagnosis of cold sores is usually based on the appearance of the lesions. Usually, no laboratory test is needed because most sores that look like cold sores are cold sores. Occasionally, mouth sores known as canker sores may be mistaken for cold sores.
However, canker sores occur inside the mouth whereas recurrent cold sores usually occur on the lips. If there is a question about the diagnosis, a variety of tests are available, including viral culture and polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
- To do these tests, a swab is rubbed over an active blister. Swabbing the blister in an attempt to culture the virus in the lab works best in the first 24-48 hours before the blister has crusted over.
- `There is also a way to test for herpes DNA in a swab that has been rubbed on the sore. This type of testing is called a “polymerase chain reaction” or PCR for short. PCR testing is very good at detecting herpes virus, but it is not as readily available as culture.
Treatment and medications
Cold sores are generally not dangerous and do not cause any permanent damage to the skin. It is also important to note that treatment will not “cure” the condition, but will treat the symptoms and may shorten the duration of the “flare up.”
Cream to treat dryness and irritation
- Aciclovir Cream—e.g. Zovirax, Chemist’s Own Cold Sore Cream
These should be applied at the first signs of a cold sore (the “tingle” stage) to help limit the attack and speed up healing. They work as an “anti-viral” fighting the herpes virus to help stop it replicating and growing. Apply 5 times a day (every 4 hours while awake) for 4-5 days. This is the preferred method of treatment as long at it is applied at the first sign of the lesion.
- Idoxuridine with lignocaine—e.g. Virasolve
Apply at first sign of cold sore—apply a thin layer to the affected area every hour on the first day, then every 4 hours until cold sore disappears. Provides good pain relief with the use of lignocaine (local anaesthetic) and keeps the lesion moist; however, please note idoxuridne has not been proven to be effective in treating the virus
- Povidone Iodine Ointment—e.g. Betadine Cold Sore Ointment
This may be applied at any stage in the cold sore cycle. This ointment may help to inactivate the virus and also reduce the spread of HSV-1 infection. Note: this product is not suitable if you have an iodine allergy. Apply liberally to the affected area at least 4 times a day.
- Protective lip balms—e.g. Carmex, Blistex, Nyal Cold Sore Cream
These often contain menthol and camphor, and act with analgesic and antiseptic qualities. They also help to keep the lesion moisturised and avoid cracking/splitting of the scab while it is in the healing stage. Do not let your cold sore dry out, as it will take longer to heal.
- L-Lysine, Zinc and Vitamin C supplements—e.g. Ethical Nutrients Lysine Viral Cold Sore Defence, Blackmores Lyp-Sine Tablets
These supplements may help to reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks of cold sores. They also act as nutritional support for a normal, healthy immune function.
- Cold sore healing patches—e.g. Compeed
These patches hide and protect the cold sore, reducing symptoms and the risk of contamination from the wound.
- Herbal/natural applications—e.g. Dynamiclear
Dynamiclear contains natural plant and mineral ingredients and is marketed as a single application liquid gel.
Activities that save spreading from one to other places of body includes:
- Avoid touching your cold sore except when applying a cold sore product
- Do not let other people touch your cold sore or come into contact with fluid from the cold sore (e.g., kissing, hugging)
- Do not touch your eyes after touching the cold sore (to avoid spreading the infection to your eyes)
- Do not share cold sore cream with others
- Do not share eating or drinking utensils, toothbrushes, towels, face cloths, razors or lipstick
- Cover your nose and mouth when coughing or sneezing, as herpes simplex can be spread by saliva
Prevention of spreading cold sore
Self-care
- If blisters have burst, keep the area clean and dry.
- The pain may be eased by applying ice to the blister.
- Follow the instructions carefully when using cold sore medicines.
- Avoid getting cold sore product in your eyes or inside your mouth.
- Wash your hands before and after applying a cold sore product.
- Avoid breaking blisters or ‘picking’ a scab, as this will delay healing and increase the risk of bacterial infection.
- Try to identify and avoid things that trigger your cold sores.
- Wear a wide brimmed hat and at least SPF 15+ sunscreen on your lips and face when in the sun.
- Learn and use relaxation techniques to relieve stress.
- Eat regular, healthy meals, including fruit, vegetables and grain foods. Limit foods high in fat, sugar or salt.
- Get enough sleep.